GenAge entry for PPARGC1A (Homo sapiens)
Entry selected based on evidence directly linking the gene product to ageing in a mammalian model organism
Gene name (HAGRID: 256)
- HGNC symbol
- PPARGC1A
- Aliases
- PGC1; PGC1A; PPARGC1
- Common name
- peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 alpha
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence directly linking the gene product to ageing in a mammalian model organism
- Description
PPARGC1A is a transcriptional coactivator that regulates and interacts with genes involved in energy metabolism [1847]. It has a role in regulating metabolism, inflammation, oxidative stress resistance and mitochondrial biogenesis and function [4340]. SIRT1 has been reported to be a functional regulator of PPARGC1A [1846].
In mice, knockout of PPARGC1A accelerates vascular aging and atherosclerosis, coinciding with telomere dysfunction and shortening and DNA damage. Expression of PPARGC1A coactivates TERT transcription and reverses telomere malfunction [4340]. In humans, PPARGC1A has been associated with cholesterol and obesity as well as age-related diseases like type 2 diabetes. Thus, PPARGC1A may play a role in in ameliorating senescence, aging, and age-associated chronic diseases.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 4p15.1
- Location
- 23,792,021 bp to 23,890,077 bp
- Orientation
- Minus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000302; response to reactive oxygen species
GO:0000422; mitophagy
GO:0001659; temperature homeostasis
GO:0001678; cellular glucose homeostasis
GO:0001933; negative regulation of protein phosphorylation
GO:0002021; response to dietary excess
GO:0002931; response to ischemia
GO:0006012; galactose metabolic process
GO:0006094; gluconeogenesis
GO:0006355; regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
GO:0006367; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter
GO:0006397; mRNA processing
GO:0006461; protein complex assembly
GO:0007005; mitochondrion organization
GO:0007568; aging
GO:0007586; digestion
GO:0007623; circadian rhythm
GO:0008209; androgen metabolic process
GO:0008380; RNA splicing
GO:0009409; response to cold
GO:0010822; positive regulation of mitochondrion organization
GO:0014732; skeletal muscle atrophy
GO:0014850; response to muscle activity
GO:0014878; response to electrical stimulus involved in regulation of muscle adaptation
GO:0014912; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell migration
GO:0019395; fatty acid oxidation
GO:0021549; cerebellum development
GO:0022904; respiratory electron transport chain
GO:0030521; androgen receptor signaling pathway
GO:0030900; forebrain development
GO:0032922; circadian regulation of gene expression
GO:0034599; cellular response to oxidative stress
GO:0035066; positive regulation of histone acetylation
GO:0035865; cellular response to potassium ion
GO:0042493; response to drug
GO:0042594; response to starvation
GO:0042752; regulation of circadian rhythm
GO:0043201; response to leucine
GO:0043524; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process
GO:0045333; cellular respiration
GO:0045722; positive regulation of gluconeogenesis
GO:0045820; negative regulation of glycolytic process
GO:0045893; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
GO:0045944; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
GO:0046321; positive regulation of fatty acid oxidation
GO:0048661; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation
GO:0048662; negative regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation
GO:0050821; protein stabilization
GO:0050873; brown fat cell differentiation
GO:0051091; positive regulation of sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity
GO:0051552; flavone metabolic process
GO:0060612; adipose tissue development
GO:0071222; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide
GO:0071250; cellular response to nitrite
GO:0071313; cellular response to caffeine
GO:0071332; cellular response to fructose stimulus
GO:0071333; cellular response to glucose stimulus
GO:0071354; cellular response to interleukin-6
GO:0071356; cellular response to tumor necrosis factor
GO:0071372; cellular response to follicle-stimulating hormone stimulus
GO:0071392; cellular response to estradiol stimulus
GO:0071456; cellular response to hypoxia
GO:0071560; cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus
GO:0071871; response to epinephrine
GO:0071873; response to norepinephrine
GO:0090258; negative regulation of mitochondrial fission
GO:0097067; cellular response to thyroid hormone stimulus
GO:1901215; negative regulation of neuron death
GO:1901558; response to metformin
GO:1901857; positive regulation of cellular respiration
GO:1901860; positive regulation of mitochondrial DNA metabolic process
GO:1901863; positive regulation of muscle tissue development
GO:1904635; positive regulation of glomerular visceral epithelial cell apoptotic process
GO:1904637; cellular response to ionomycin
GO:1904639; cellular response to resveratrol
GO:1904640; response to methionine
GO:1990845; adaptive thermogenesis
GO:2000184; positive regulation of progesterone biosynthetic process
GO:2000272; negative regulation of receptor activity
GO:2000310; regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate selective glutamate receptor activity
GO:2000507; positive regulation of energy homeostasis
GO:2001171; positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process
Cellular component: GO:0005634; nucleus
GO:0005654; nucleoplasm
GO:0005665; DNA-directed RNA polymerase II, core complex
GO:0005719; nuclear euchromatin
GO:0016605; PML body
GO:0022626; cytosolic ribosome
GO:0043025; neuronal cell body
GO:0097440; apical dendrite
GO:1990843; subsarcolemmal mitochondrion
GO:1990844; interfibrillar mitochondrion
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0000166; nucleotide binding
GO:0001104; RNA polymerase II transcription cofactor activity
GO:0003677; DNA binding
GO:0003713; transcription coactivator activity
GO:0003723; RNA binding
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0008134; transcription factor binding
GO:0016922; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor binding
GO:0030331; estrogen receptor binding
GO:0030374; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor transcription coactivator activity
GO:0031490; chromatin DNA binding
GO:0031625; ubiquitin protein ligase binding
GO:0042975; peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding
GO:0043014; alpha-tubulin binding
GO:0043565; sequence-specific DNA binding
GO:0050681; androgen receptor binding
GO:1990841; promoter-specific chromatin binding
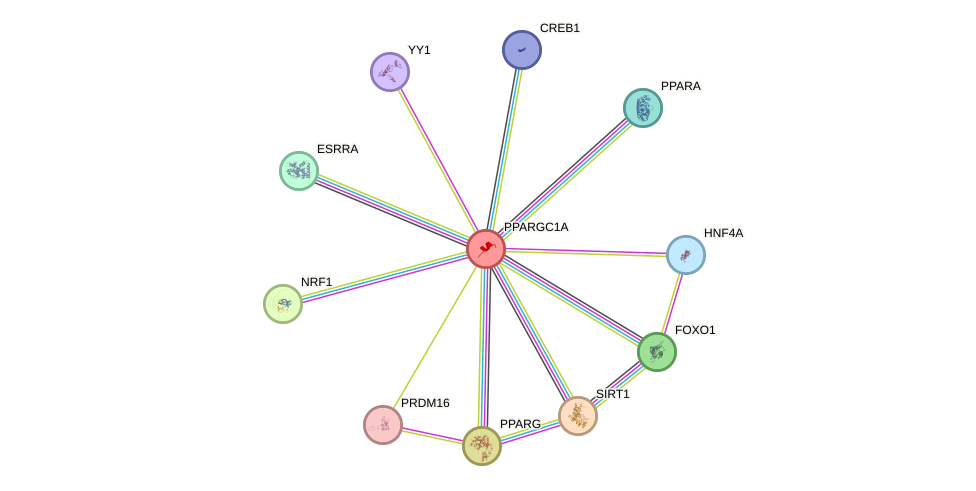
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- TP53, EGFR, PPARA, CREBBP, NR3C1, NFKB1, UBE2I, EP300, PML, GSK3B, RELA, SIRT1, MED1, ESR1, PPARG
- STRING interaction network