GenAge entry for ATM (Homo sapiens)
Entry selected based on evidence directly linking the gene product to ageing in a mammalian model organism
Gene name (HAGRID: 9)
- HGNC symbol
- ATM
- Aliases
- TEL1; TELO1; ATA; ATDC; ATC; ATD
- Common name
- ATM serine/threonine kinase
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence directly linking the gene product to ageing in a mammalian model organism
- Description
ATM is involved diverse aspects of cellular physiology including DNA repair and cell cycle control. It appears to activate DNA repair pathways in response to DNA damage [35]. Mutations in human ATM cause ataxia telangiectasia [190], an early-onset disease some argue is characterized by signs of premature ageing [238]. Patients display cerebellar atrophy and neurodegeneration.
In mouse and worm models that are ATM deficient replenishing intracellular NAD+ reduces the severity of neuropathy, normalizes neuromuscular function, delays memory loss, and extends lifespan [4365]. In mice, mutations in ATM in late-generation TERC mutants with short telomeres results in signs of premature ageing starting at about 6 months of age [12]. In mouse and human cells ATM is required for the recruitment of telomerase and inhibition of ATM leads to shortening of telomeres [4494][4495]. However, it has also been shown that inhibiting ATM attenuates senescence. Inhibiting ATM induces the functional recovery of the lysosome/autophagy system and accelerates the removal of dysfunctional mitochondria [4496]. Overall, it is possible ATM plays a role in human ageing and may link two major theories on ageing: DNA damage accumulation and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 11q22-q23
- Location
- 108,222,832 bp to 108,369,099 bp
- Orientation
- Plus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000724; double-strand break repair via homologous recombination
GO:0000729; DNA double-strand break processing
GO:0000731; DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair
GO:0000732; strand displacement
GO:0001541; ovarian follicle development
GO:0001666; response to hypoxia
GO:0001756; somitogenesis
GO:0002331; pre-B cell allelic exclusion
GO:0002377; immunoglobulin production
GO:0006260; DNA replication
GO:0006281; DNA repair
GO:0006303; double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining
GO:0006468; protein phosphorylation
GO:0006974; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
GO:0006975; DNA damage induced protein phosphorylation
GO:0006977; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest
GO:0007004; telomere maintenance via telomerase
GO:0007050; cell cycle arrest
GO:0007094; mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint
GO:0007131; reciprocal meiotic recombination
GO:0007140; male meiosis
GO:0007143; female meiotic division
GO:0007165; signal transduction
GO:0007420; brain development
GO:0007507; heart development
GO:0008340; determination of adult lifespan
GO:0008630; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage
GO:0009791; post-embryonic development
GO:0010212; response to ionizing radiation
GO:0010506; regulation of autophagy
GO:0016572; histone phosphorylation
GO:0018105; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
GO:0030889; negative regulation of B cell proliferation
GO:0032212; positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase
GO:0033129; positive regulation of histone phosphorylation
GO:0033151; V(D)J recombination
GO:0035264; multicellular organism growth
GO:0036092; phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate biosynthetic process
GO:0036289; peptidyl-serine autophosphorylation
GO:0042159; lipoprotein catabolic process
GO:0042981; regulation of apoptotic process
GO:0043065; positive regulation of apoptotic process
GO:0043517; positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator
GO:0043525; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process
GO:0045141; meiotic telomere clustering
GO:0046777; protein autophosphorylation
GO:0048538; thymus development
GO:0048599; oocyte development
GO:0051402; neuron apoptotic process
GO:0051972; regulation of telomerase activity
GO:0071044; histone mRNA catabolic process
GO:0071480; cellular response to gamma radiation
GO:0071481; cellular response to X-ray
GO:0071500; cellular response to nitrosative stress
GO:0072434; signal transduction involved in mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint
GO:0090399; replicative senescence
GO:0097694; establishment of RNA localization to telomere
GO:0097695; establishment of macromolecular complex localization to telomere
GO:1900034; regulation of cellular response to heat
GO:1901796; regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator
GO:1904262; negative regulation of TORC1 signaling
GO:1904354; negative regulation of telomere capping
GO:1904358; positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomere lengthening
GO:1904884; positive regulation of telomerase catalytic core complex assembly
Cellular component: GO:0000781; chromosome, telomeric region
GO:0000784; nuclear chromosome, telomeric region
GO:0005634; nucleus
GO:0005654; nucleoplasm
GO:0005819; spindle
GO:0031410; cytoplasmic vesicle
GO:1990391; DNA repair complex
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0003677; DNA binding
GO:0004674; protein serine/threonine kinase activity
GO:0004677; DNA-dependent protein kinase activity
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0005524; ATP binding
GO:0016303; 1-phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase activity
GO:0032403; protein complex binding
GO:0046983; protein dimerization activity
GO:0047485; protein N-terminus binding
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
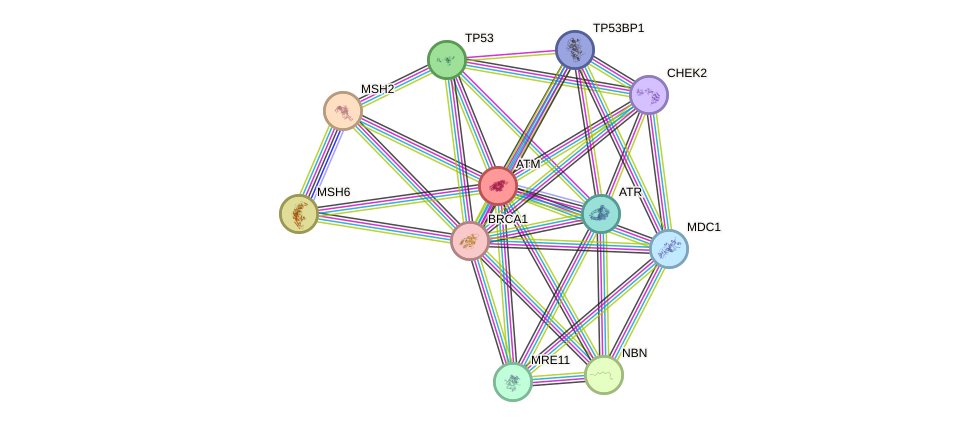
- TP53, ATM, WRN, PEX5, PARP1, BRCA1, HIF1A, RPA1, BLM, ABL1, BRCA2, TOP1, RAD51, TERF1, PRKDC, XRCC5, TERF2, HSPA8, FOXO3, XPA, HDAC1, MAPK14, MED1, BMI1, CREB1, ATF2, E2F1, MDM2, TAF1, RELA, NBN, H2AFX, PPP1CA, ATR, MLH1, CHEK2, SIRT7, TP53BP1
- STRING interaction network
Retrieve sequences for ATM
Homologs in model organisms
In other databases
- GenAge model organism genes
- A homolog of this gene for Mus musculus is present as Atm
- LongevityMap
- This gene is present as ATM
- CellAge
- This gene is present as ATM