GenAge entry for XPA (Homo sapiens)
Gene name (HAGRID: 126)
- HGNC symbol
- XPA
- Aliases
- XPAC; XP1
- Common name
- xeroderma pigmentosum, complementation group A
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence linking the gene product to a pathway or mechanism linked to ageing
- Description
XPA is primarily involved in DNA repair. In mice, mutations in both XPA and ERCC2 result in a phenotype resembling accelerated ageing with animals living about 5 months, but because mutations in ERCC2 alone also result in accelerated ageing, it is not clear to what extent the XPA gene contributes to the accelerated ageing phenotype [14]. In fact, mice lacking XPA do not appear to age faster [494]. Mice mutant for XPA and ERCC6 die before weaning and display some signs of premature ageing included stunted growth, neurological dysfunction, retinal degeneration, cachexia, and kyphosis [1934]. In humans, XPA has been associated with cancer [396], though it is possible XPA also plays some role in human ageing.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 9q22.3
- Location
- 97,674,909 bp to 97,697,409 bp
- Orientation
- Minus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000715; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA damage recognition
GO:0000717; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA duplex unwinding
GO:0006283; transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair
GO:0006284; base-excision repair
GO:0006293; nucleotide-excision repair, preincision complex stabilization
GO:0006294; nucleotide-excision repair, preincision complex assembly
GO:0006295; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA incision, 3'-to lesion
GO:0006296; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA incision, 5'-to lesion
GO:0006979; response to oxidative stress
GO:0008630; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage
GO:0009636; response to toxic substance
GO:0010996; response to auditory stimulus
GO:0033683; nucleotide-excision repair, DNA incision
GO:0035264; multicellular organism growth
GO:0070911; global genome nucleotide-excision repair
GO:0070914; UV-damage excision repair
GO:1901255; nucleotide-excision repair involved in interstrand cross-link repair
Cellular component: GO:0000110; nucleotide-excision repair factor 1 complex
GO:0005634; nucleus
GO:0005654; nucleoplasm
GO:0005662; DNA replication factor A complex
GO:0005737; cytoplasm
GO:0005794; Golgi apparatus
GO:0045171; intercellular bridge
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0003684; damaged DNA binding
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0019904; protein domain specific binding
GO:0042803; protein homodimerization activity
GO:0046872; metal ion binding
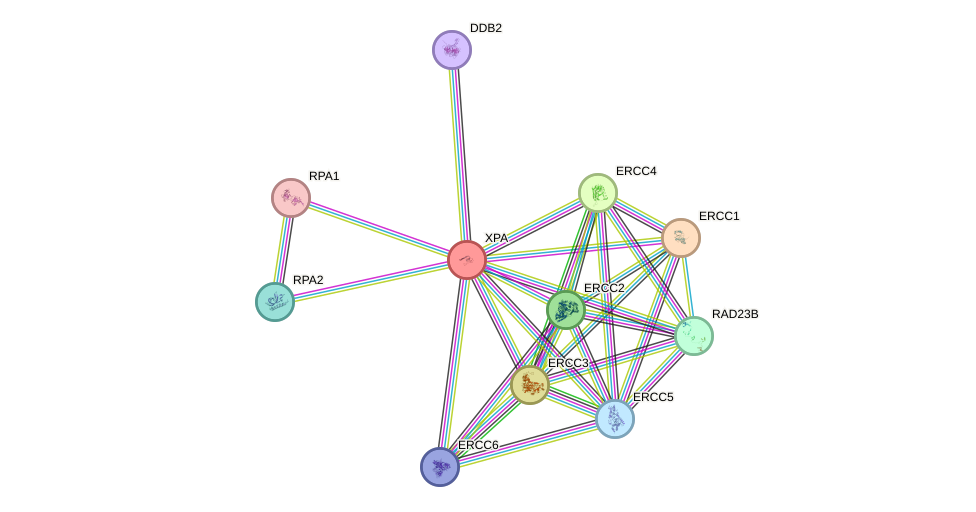
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- ATM, RPA1, ERCC6, EP300, PRKDC, ERCC1, HMGB1, ATR, ERCC4
- STRING interaction network
Retrieve sequences for XPA
Homologs in model organisms
- Caenorhabditis elegans
- xpa-1
- Drosophila melanogaster
- Xpac
- Mus musculus
- Xpa
- Rattus norvegicus
- Xpa
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- RAD14
- Schizosaccharomyces pombe
- rhp14
In other databases
- GenAge model organism genes
- A homolog of this gene for Mus musculus is present as Xpa
- LongevityMap
- This gene is present as XPA