GenAge entry for RECQL4 (Homo sapiens)
Gene name (HAGRID: 128)
- HGNC symbol
- RECQL4
- Aliases
- RecQ4
- Common name
- RecQ helicase-like 4
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence linking the gene product to a pathway or mechanism linked to ageing
- Description
A helicase that is responsibility for a majority of the cases of Rothmund-Thomson syndrome [651][4490], RECQL4 belongs to the same family of WRN and BLM. Though Rothmund-Thomson syndrome does not resemble accelerated ageing like Werner's syndrome does [444], it is reasonable that RECQL4 might be involved in human ageing. RECQL4 participates in multiple DNA pathways [4490] and cells from patients carrying RECQL4 mutations can exhibit elevated stress-induced premature senescence [4491]. RECQL4-deficient mice die at embryonic stages [1692].
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 8q24.3
- Location
- 144,511,284 bp to 144,517,826 bp
- Orientation
- Minus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000733; DNA strand renaturation
GO:0006260; DNA replication
GO:0006281; DNA repair
GO:0006284; base-excision repair
GO:0006302; double-strand break repair
GO:0006310; DNA recombination
GO:0007275; multicellular organism development
GO:0032508; DNA duplex unwinding
Cellular component: GO:0005634; nucleus
GO:0005694; chromosome
GO:0005737; cytoplasm
GO:0016020; membrane
Show all GO termsFunction: GO:0000405; bubble DNA binding
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0005524; ATP binding
GO:0009378; four-way junction helicase activity
GO:0036310; annealing helicase activity
GO:0043140; ATP-dependent 3'-5' DNA helicase activity
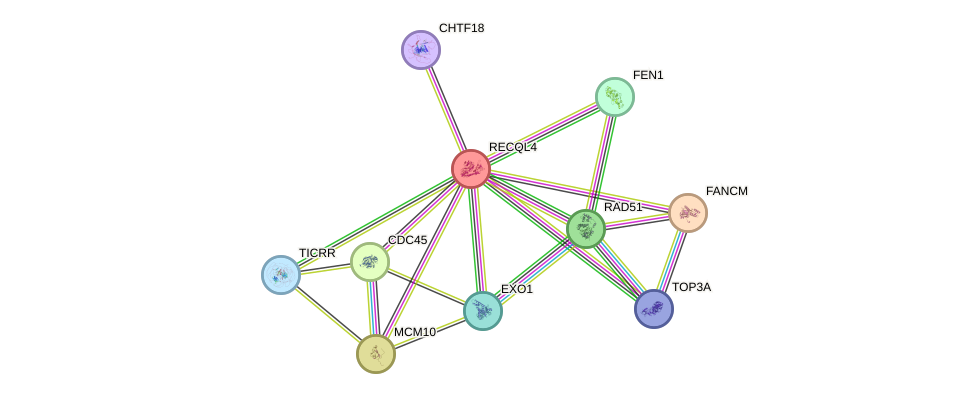
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- EP300, TERF1, SIRT1, MAPK14
- STRING interaction network