GenAge entry for CEBPB (Homo sapiens)
Entry selected based on evidence directly linking the gene product to ageing in a mammalian model organism
Gene name (HAGRID: 89)
- HGNC symbol
- CEBPB
- Aliases
- LAP; CRP2; NFIL6; IL6DBP; C/EBP-beta; TCF5
- Common name
- CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence directly linking the gene product to ageing in a mammalian model organism
- Description
Like CEBPA, CEBPB is a transcription factor involved in fat metabolism. CEBPB also appears to play a role in liver regeneration [1130]. Albeit it was not clear their ageing process was retarded, mice carrying the CEBPB gene instead of CEBPA lived 20% more than controls, burned more fat, and their mitochondria were more active [1122]. As such, it is possible that CEBPB plays a role in human ageing, though further studies are necessary to confirm this hypothesis.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 20q13.1
- Location
- 50,190,583 bp to 50,192,691 bp
- Orientation
- Plus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0001541; ovarian follicle development
GO:0001892; embryonic placenta development
GO:0006355; regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
GO:0006366; transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
GO:0006953; acute-phase response
GO:0006954; inflammatory response
GO:0006955; immune response
GO:0007613; memory
GO:0030182; neuron differentiation
GO:0032753; positive regulation of interleukin-4 production
GO:0033598; mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation
GO:0034976; response to endoplasmic reticulum stress
GO:0042130; negative regulation of T cell proliferation
GO:0042742; defense response to bacterium
GO:0043524; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process
GO:0045408; regulation of interleukin-6 biosynthetic process
GO:0045600; positive regulation of fat cell differentiation
GO:0045669; positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation
GO:0045670; regulation of osteoclast differentiation
GO:0045892; negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
GO:0045944; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
GO:0050873; brown fat cell differentiation
GO:0060644; mammary gland epithelial cell differentiation
GO:0060850; regulation of transcription involved in cell fate commitment
GO:0070059; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress
GO:0071222; cellular response to lipopolysaccharide
GO:0071230; cellular response to amino acid stimulus
GO:0071347; cellular response to interleukin-1
GO:0071407; cellular response to organic cyclic compound
GO:0072574; hepatocyte proliferation
GO:0097421; liver regeneration
GO:1990440; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress
Cellular component: GO:0000779; condensed chromosome, centromeric region
GO:0000790; nuclear chromatin
GO:0005634; nucleus
GO:0005654; nucleoplasm
GO:0005737; cytoplasm
GO:0016363; nuclear matrix
GO:0036488; CHOP-C/EBP complex
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0000977; RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
GO:0000978; RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding
GO:0000979; RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding
GO:0001077; transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding
GO:0003677; DNA binding
GO:0003682; chromatin binding
GO:0003700; transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding
GO:0003705; transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II distal enhancer sequence-specific binding
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0008134; transcription factor binding
GO:0019900; kinase binding
GO:0035035; histone acetyltransferase binding
GO:0035259; glucocorticoid receptor binding
GO:0042803; protein homodimerization activity
GO:0042826; histone deacetylase binding
GO:0044389; ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding
GO:0046982; protein heterodimerization activity
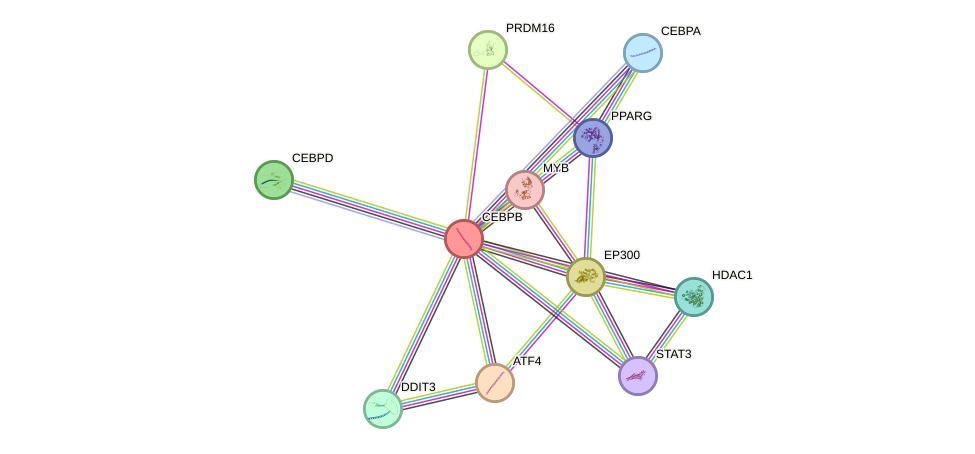
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- STAT3, MYC, EGFR, NCOR1, BRCA1, CREBBP, NR3C1, EGR1, NFKB1, CEBPA, CEBPB, EP300, GSK3B, AR, RB1, FOXO1, HSF1, RELA, HDAC1, SP1, JUN, CREB1, ATF2, DDIT3, ESR1, TP63, PPARG, NCOR2
- STRING interaction network
Retrieve sequences for CEBPB
Homologs in model organisms
In other databases
- GenAge model organism genes
- A homolog of this gene for Mus musculus is present as Cebpb
- GenAge microarray genes
- This gene is present as CEBPB
- CellAge
- This gene is present as CEBPB