GenAge entry for INS (Homo sapiens)
Gene name (HAGRID: 30)
- HGNC symbol
- INS
- Aliases
- IDDM2; IDDM1
- Common name
- insulin
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence linking the gene product to a pathway or mechanism linked to ageing
- Description
Insulin is produced by cells in the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas. It decreases blood glucose concentration and regulates the cellular metabolism of monosaccharides, amino acids and fatty acids.
As with IGF1, INS may be involved in the ageing process of model organisms [284]. In roundworms, expression of the human insulin gene enhances dauer formation and slightly increases lifespan [960]. Despite the well-established age-related onset of type 2 diabetes, and possible roles of INS in other age-related diseases [312], the impact of INS on human ageing is unclear.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 11p15.5
- Location
- 2,159,778 bp to 2,161,209 bp
- Orientation
- Minus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000165; MAPK cascade
GO:0002674; negative regulation of acute inflammatory response
GO:0006006; glucose metabolic process
GO:0006355; regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
GO:0006521; regulation of cellular amino acid metabolic process
GO:0006888; ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport
GO:0006953; acute-phase response
GO:0007186; G-protein coupled receptor signaling pathway
GO:0007267; cell-cell signaling
GO:0008284; positive regulation of cell proliferation
GO:0008286; insulin receptor signaling pathway
GO:0010628; positive regulation of gene expression
GO:0014068; positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling
GO:0015758; glucose transport
GO:0022898; regulation of transmembrane transporter activity
GO:0030307; positive regulation of cell growth
GO:0030335; positive regulation of cell migration
GO:0031954; positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation
GO:0032148; activation of protein kinase B activity
GO:0032270; positive regulation of cellular protein metabolic process
GO:0032460; negative regulation of protein oligomerization
GO:0032880; regulation of protein localization
GO:0033861; negative regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity
GO:0042060; wound healing
GO:0042177; negative regulation of protein catabolic process
GO:0042593; glucose homeostasis
GO:0043410; positive regulation of MAPK cascade
GO:0044267; cellular protein metabolic process
GO:0045429; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process
GO:0045597; positive regulation of cell differentiation
GO:0045721; negative regulation of gluconeogenesis
GO:0045725; positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process
GO:0045740; positive regulation of DNA replication
GO:0045818; negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process
GO:0045821; positive regulation of glycolytic process
GO:0045840; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division
GO:0045861; negative regulation of proteolysis
GO:0045908; negative regulation of vasodilation
GO:0045909; positive regulation of vasodilation
GO:0045922; negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process
GO:0046326; positive regulation of glucose import
GO:0046628; positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway
GO:0046631; alpha-beta T cell activation
GO:0046889; positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process
GO:0050708; regulation of protein secretion
GO:0050709; negative regulation of protein secretion
GO:0050715; positive regulation of cytokine secretion
GO:0050731; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
GO:0050995; negative regulation of lipid catabolic process
GO:0051000; positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity
GO:0051092; positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity
GO:0051897; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling
GO:0055089; fatty acid homeostasis
GO:0060266; negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response
GO:0060267; positive regulation of respiratory burst
GO:0090277; positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion
GO:0090336; positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation
GO:1900182; positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus
GO:1902176; negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:2000252; negative regulation of feeding behavior
Cellular component: GO:0000139; Golgi membrane
GO:0005576; extracellular region
GO:0005615; extracellular space
GO:0005788; endoplasmic reticulum lumen
GO:0005796; Golgi lumen
GO:0030133; transport vesicle
GO:0031904; endosome lumen
GO:0033116; endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane
GO:0034774; secretory granule lumen
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0002020; protease binding
GO:0005158; insulin receptor binding
GO:0005159; insulin-like growth factor receptor binding
GO:0005179; hormone activity
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0042802; identical protein binding
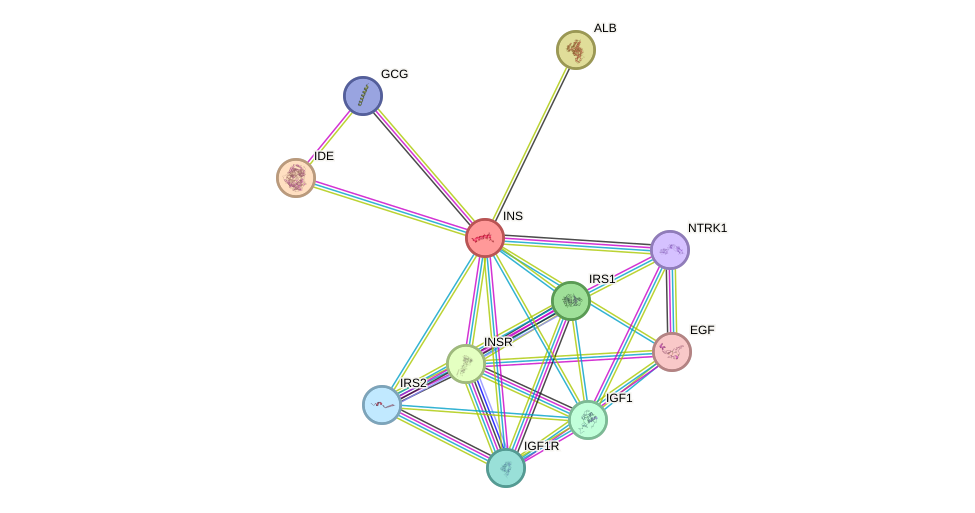
Protein interactions and network
Retrieve sequences for INS
Homologs in model organisms
In other databases
- LongevityMap
- This gene is present as INS