GenAge entry for BCL2 (Homo sapiens)
Gene name (HAGRID: 69)
- HGNC symbol
- BCL2
- Aliases
- Bcl-2; PPP1R50
- Common name
- B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence linking the gene product to a pathway or mechanism linked to ageing
- Description
BCL2 is an important suppressor of apoptosis and an oncogene. Apart from cancer, it may be involved in neurodegenerative disorders [447], and dendritic cell longevity in vivo has been reported to be controlled by BCL2 [1110]. BCL2 null mice die by six weeks of age with occurrence of grey hair though otherwise they do not appear to suffer from accelerated ageing [449]. In addition, some researchers have argued that BCL2's role in apoptosis suggests an involvement of BCL2 in ageing [942]. More detailed studies are necessary to investigate this possibility.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 18q21.3
- Location
- 63,123,346 bp to 63,319,380 bp
- Orientation
- Minus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000209; protein polyubiquitination
GO:0001503; ossification
GO:0001541; ovarian follicle development
GO:0001656; metanephros development
GO:0001658; branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis
GO:0001662; behavioral fear response
GO:0001782; B cell homeostasis
GO:0001836; release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
GO:0001952; regulation of cell-matrix adhesion
GO:0002320; lymphoid progenitor cell differentiation
GO:0002326; B cell lineage commitment
GO:0002931; response to ischemia
GO:0003014; renal system process
GO:0006470; protein dephosphorylation
GO:0006582; melanin metabolic process
GO:0006808; regulation of nitrogen utilization
GO:0006915; apoptotic process
GO:0006959; humoral immune response
GO:0006974; cellular response to DNA damage stimulus
GO:0007015; actin filament organization
GO:0007409; axonogenesis
GO:0007565; female pregnancy
GO:0007569; cell aging
GO:0008584; male gonad development
GO:0008625; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors
GO:0008630; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage
GO:0008631; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to oxidative stress
GO:0009314; response to radiation
GO:0009636; response to toxic substance
GO:0009791; post-embryonic development
GO:0010039; response to iron ion
GO:0010224; response to UV-B
GO:0010332; response to gamma radiation
GO:0010468; regulation of gene expression
GO:0010507; negative regulation of autophagy
GO:0010523; negative regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol
GO:0010559; regulation of glycoprotein biosynthetic process
GO:0014031; mesenchymal cell development
GO:0014042; positive regulation of neuron maturation
GO:0014911; positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration
GO:0016049; cell growth
GO:0018105; peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
GO:0018107; peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation
GO:0021747; cochlear nucleus development
GO:0022612; gland morphogenesis
GO:0022898; regulation of transmembrane transporter activity
GO:0030279; negative regulation of ossification
GO:0030307; positive regulation of cell growth
GO:0030308; negative regulation of cell growth
GO:0030318; melanocyte differentiation
GO:0030336; negative regulation of cell migration
GO:0030890; positive regulation of B cell proliferation
GO:0031069; hair follicle morphogenesis
GO:0031103; axon regeneration
GO:0031647; regulation of protein stability
GO:0032469; endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis
GO:0032835; glomerulus development
GO:0032848; negative regulation of cellular pH reduction
GO:0033033; negative regulation of myeloid cell apoptotic process
GO:0033077; T cell differentiation in thymus
GO:0033138; positive regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
GO:0033689; negative regulation of osteoblast proliferation
GO:0034097; response to cytokine
GO:0035094; response to nicotine
GO:0035265; organ growth
GO:0040018; positive regulation of multicellular organism growth
GO:0042100; B cell proliferation
GO:0042149; cellular response to glucose starvation
GO:0042493; response to drug
GO:0042542; response to hydrogen peroxide
GO:0043029; T cell homeostasis
GO:0043066; negative regulation of apoptotic process
GO:0043085; positive regulation of catalytic activity
GO:0043375; CD8-positive, alpha-beta T cell lineage commitment
GO:0043496; regulation of protein homodimerization activity
GO:0043497; regulation of protein heterodimerization activity
GO:0043524; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process
GO:0043583; ear development
GO:0045069; regulation of viral genome replication
GO:0045636; positive regulation of melanocyte differentiation
GO:0046671; negative regulation of retinal cell programmed cell death
GO:0046902; regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability
GO:0048041; focal adhesion assembly
GO:0048536; spleen development
GO:0048538; thymus development
GO:0048546; digestive tract morphogenesis
GO:0048599; oocyte development
GO:0048743; positive regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development
GO:0048753; pigment granule organization
GO:0048873; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue
GO:0050853; B cell receptor signaling pathway
GO:0051384; response to glucocorticoid
GO:0051402; neuron apoptotic process
GO:0051607; defense response to virus
GO:0051881; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential
GO:0051902; negative regulation of mitochondrial depolarization
GO:0051924; regulation of calcium ion transport
GO:0055085; transmembrane transport
GO:0070059; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress
GO:0071310; cellular response to organic substance
GO:0071456; cellular response to hypoxia
GO:0072593; reactive oxygen species metabolic process
GO:0097192; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand
GO:1900740; positive regulation of protein insertion into mitochondrial membrane involved in apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:2000134; negative regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle
GO:2000378; negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process
GO:2000811; negative regulation of anoikis
GO:2001234; negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:2001240; negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand
GO:2001243; negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:2001244; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
Cellular component: GO:0005634; nucleus
GO:0005737; cytoplasm
GO:0005739; mitochondrion
GO:0005741; mitochondrial outer membrane
GO:0005783; endoplasmic reticulum
GO:0005789; endoplasmic reticulum membrane
GO:0005829; cytosol
GO:0016020; membrane
GO:0031965; nuclear membrane
GO:0043209; myelin sheath
GO:0046930; pore complex
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0002020; protease binding
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0008134; transcription factor binding
GO:0015267; channel activity
GO:0016248; channel inhibitor activity
GO:0031625; ubiquitin protein ligase binding
GO:0042802; identical protein binding
GO:0042803; protein homodimerization activity
GO:0043565; sequence-specific DNA binding
GO:0046982; protein heterodimerization activity
GO:0051434; BH3 domain binding
GO:0051721; protein phosphatase 2A binding
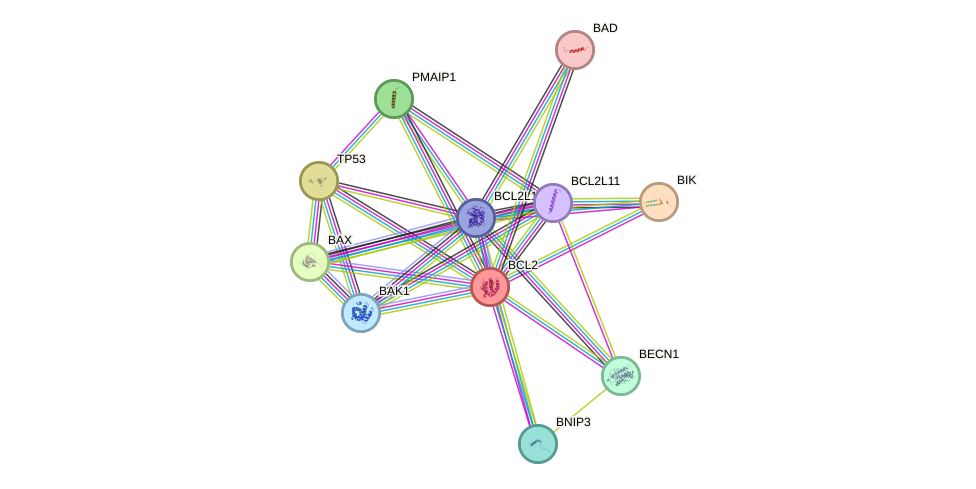
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- TP53, IRS1, IRS2, MYC, PPARA, PARP1, BRCA1, PIN1, HIF1A, BCL2, HSP90AA1, UBE2I, PML, BAX, SOD1, HSPA1A, MAPK8, CDK1, PSEN1, PPP1CA, CISD2, BAK1, IKBKB, SQSTM1
- STRING interaction network
Retrieve sequences for BCL2
Homologs in model organisms
In other databases
- CellAge
- This gene is present as BCL2