GenAge entry for INSR (Homo sapiens)
Gene name (HAGRID: 42)
- HGNC symbol
- INSR
- Aliases
- CD220
- Common name
- insulin receptor
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence directly linking the gene product to ageing in a non-mammalian animal model
- Description
INSR binds insulin (INS) and regulates energy metabolism [1108]. Evidence from model organisms, including results from fruit flies [187] and roundworms [539], relates INSR homologues to ageing, most likely as part of the GH1/IGF1 axis. In mice, disruption of INSR in adipose tissue extends longevity but does not appear to delay ageing [178]. In flies, the two most common alleles (InRlong and InRshort) are associated with predictable differences in levels of insulin signaling, fecundity, development time, body size, and stress tolerance (temperature and starvation) [3657]. Flies carrying the InRshort and InRlong alleles generally showed little difference in rates of aging, with InRshort males displaying a reduced mortality late in life. Heterozygotes in both sexes live significantly longer than homozygote genotypes [3657]. Mutations in the human INSR gene have been associated with insulin resistance [1661]. INSR could play a role in some human age-related pathologies, but it is not known whether it is a major player in human ageing.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 19p13
- Location
- 7,112,255 bp to 7,294,000 bp
- Orientation
- Minus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000187; activation of MAPK activity
GO:0001934; positive regulation of protein phosphorylation
GO:0003007; heart morphogenesis
GO:0005975; carbohydrate metabolic process
GO:0006355; regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
GO:0007186; G-protein coupled receptor signaling pathway
GO:0008284; positive regulation of cell proliferation
GO:0008286; insulin receptor signaling pathway
GO:0008544; epidermis development
GO:0008584; male gonad development
GO:0018108; peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
GO:0019087; transformation of host cell by virus
GO:0023014; signal transduction by protein phosphorylation
GO:0030238; male sex determination
GO:0030325; adrenal gland development
GO:0030335; positive regulation of cell migration
GO:0031017; exocrine pancreas development
GO:0032147; activation of protein kinase activity
GO:0032148; activation of protein kinase B activity
GO:0032869; cellular response to insulin stimulus
GO:0038083; peptidyl-tyrosine autophosphorylation
GO:0042593; glucose homeostasis
GO:0043410; positive regulation of MAPK cascade
GO:0045429; positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process
GO:0045725; positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process
GO:0045740; positive regulation of DNA replication
GO:0045821; positive regulation of glycolytic process
GO:0045840; positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division
GO:0045893; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
GO:0045995; regulation of embryonic development
GO:0046326; positive regulation of glucose import
GO:0046777; protein autophosphorylation
GO:0048639; positive regulation of developmental growth
GO:0051290; protein heterotetramerization
GO:0051446; positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle
GO:0051897; positive regulation of protein kinase B signaling
GO:0060267; positive regulation of respiratory burst
GO:0071363; cellular response to growth factor stimulus
GO:2000194; regulation of female gonad development
Cellular component: GO:0005886; plasma membrane
GO:0005887; integral component of plasma membrane
GO:0005899; insulin receptor complex
GO:0005901; caveola
GO:0010008; endosome membrane
GO:0016020; membrane
GO:0043231; intracellular membrane-bounded organelle
GO:0043235; receptor complex
GO:0070062; extracellular exosome
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0004713; protein tyrosine kinase activity
GO:0004716; signal transducer, downstream of receptor, with protein tyrosine kinase activity
GO:0005009; insulin-activated receptor activity
GO:0005159; insulin-like growth factor receptor binding
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0005524; ATP binding
GO:0005525; GTP binding
GO:0031994; insulin-like growth factor I binding
GO:0031995; insulin-like growth factor II binding
GO:0043548; phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding
GO:0043559; insulin binding
GO:0043560; insulin receptor substrate binding
GO:0051425; PTB domain binding
Protein interactions and network
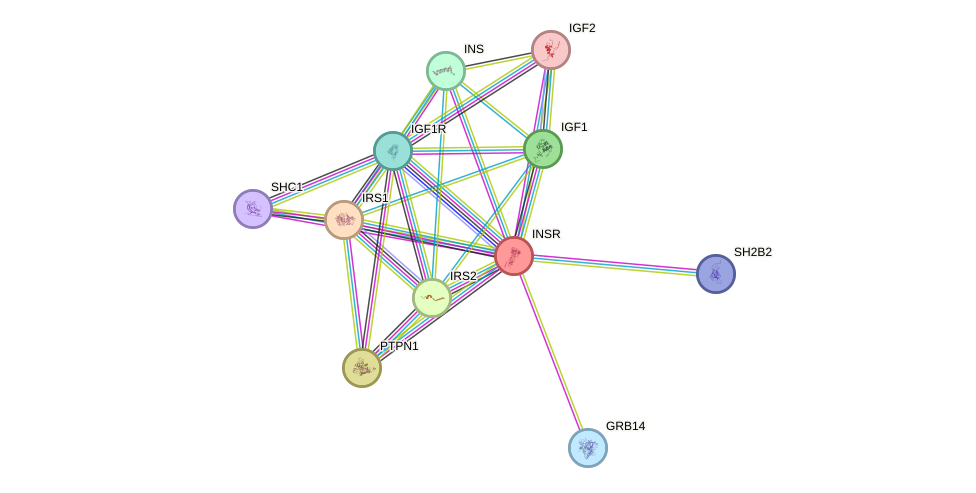
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- SHC1, PTPN11, STAT5B, STAT5A, IRS1, PTPN1, IRS2, HRAS, PRKCD, GRB2, MAPK3, JAK2, SQSTM1
- STRING interaction network
Retrieve sequences for INSR
Homologs in model organisms
In other databases
- GenAge model organism genes
- A homolog of this gene for Mus musculus is present as Insr
- LongevityMap
- This gene is present as INSR