GenAge entry for APOE (Homo sapiens)
Gene name (HAGRID: 138)
- HGNC symbol
- APOE
- Aliases
- AD2
- Common name
- apolipoprotein E
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence linking the gene or its product to human longevity and/or multiple age-related phenotypes
- Description
APOE is involved in lipid metabolism. Mice without APOE show dysregulations in lipid metabolism, having higher plasma cholesterol levels and developing arterial lesions [699], displaying DNA oxidative stress at a hepatic level [3602], and presenting severe atherosclerosis and cutaneous xanthomatosis [2138]. They also have a significantly shorter lifespan than wild-type [2138]. Neurodegeneration has also been reported in APOE-null mice [1699].
Several polymorphisms in the human APOE gene have been associated with diseases, such as increased risk of myocardial infarction [1700] and Alzheimer’s disease [4497]. Polymorphisms in APOE have been linked to human longevity [145]. There are four isoforms of APOE in humans. In Alzheimer’s disease the ApoE2 isoform is protective and the ApoE4 isoform is causative and stimulates amyloid beta production [4497]. ApoE4 also exacerbates tauopathy in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease and ApoE4 knock-in mice show significantly higher levels of tau in the brain [4498]. Despite its association with age-related disease the ApoE4 isoform is the second most common after the ApoE3 isoform and is the ancestral form of APOE [4499]. Clearly, APOE has an impact on various age-related diseases, such as atherosclerosis and neurodegeneration, but its overall impact on the human ageing process remains to be determined.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 19q13.2
- Location
- 44,905,748 bp to 44,909,395 bp
- Orientation
- Plus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000302; response to reactive oxygen species
GO:0001523; retinoid metabolic process
GO:0001937; negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation
GO:0002021; response to dietary excess
GO:0006641; triglyceride metabolic process
GO:0006707; cholesterol catabolic process
GO:0006874; cellular calcium ion homeostasis
GO:0006898; receptor-mediated endocytosis
GO:0007010; cytoskeleton organization
GO:0007186; G-protein coupled receptor signaling pathway
GO:0007263; nitric oxide mediated signal transduction
And 63 more GO terms Cellular component: GO:0005576; extracellular region
GO:0005615; extracellular space
GO:0005634; nucleus
GO:0005737; cytoplasm
GO:0005769; early endosome
GO:0005783; endoplasmic reticulum
GO:0005794; Golgi apparatus
GO:0005886; plasma membrane
GO:0016020; membrane
GO:0030425; dendrite
GO:0031012; extracellular matrix
And 11 more GO terms
Show all GO termsFunction: GO:0001540; beta-amyloid binding
GO:0005319; lipid transporter activity
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0005543; phospholipid binding
GO:0008201; heparin binding
GO:0008289; lipid binding
GO:0015485; cholesterol binding
GO:0016209; antioxidant activity
GO:0017127; cholesterol transporter activity
GO:0042802; identical protein binding
GO:0042803; protein homodimerization activity
And 7 more GO terms
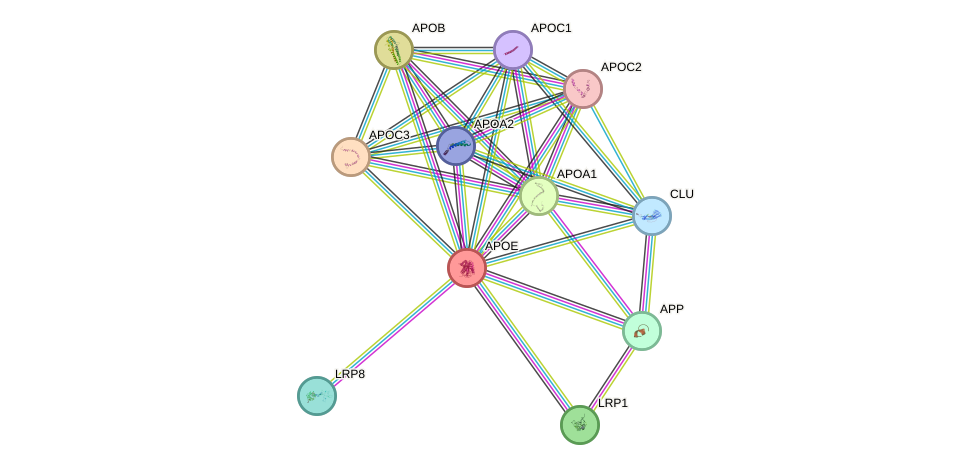
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- LRP2, APOE, A2M, PCMT1, MAPT, PSEN1
- STRING interaction network
Retrieve sequences for APOE
Homologs in model organisms
In other databases
- GenAge model organism genes
- A homolog of this gene for Mus musculus is present as Apoe
- GenAge microarray genes
- This gene is present as APOE
- LongevityMap
- This gene is present as APOE