GenAge entry for GHR (Homo sapiens)
Entry selected based on evidence directly linking the gene product to ageing in a mammalian model organism
Gene name (HAGRID: 1)
- HGNC symbol
- GHR
- Aliases
- GHBP
- Common name
- growth hormone receptor
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence directly linking the gene product to ageing in a mammalian model organism
- Description
Growth hormone (GH1) binds GHR to activate an intracellular signal transduction pathway that leads to the synthesis and secretion of IGF1. The GHR gene also encodes a soluble form called growth hormone binding protein (GHBP) that binds GH1 and likely serves as a reservoir of GH1 in the plasma.
Disruption of GHR causes dwarfism in mice, enhances insulin (INS) sensitivity, and significantly extends longevity [3]. Mice with disrupted GHR (GHRKO) do not live longer when subjected to calorie restriction, which suggests a role for GHR and possibly the associated GH1/IGF1 signalling in caloric restriction [1773]. Mice where GHR is interrupted in adulthood (aGHRKO) display many of the same traits as GHR knockout mice including reduced growth, high adiposity and enhanced INS sensitivity. However, only female animals show an increase in their maximal lifespan, the lifespan of male aGHRKO mice do not differ from the controls [4335]. Ames mice, which lack GH1 due to a mutation in PROP1, have increased health span and lifespan. Ames mice have been crossbred with GHRKO mice, producing a new lineage lacking both GH1 and the GHR. These mice have improved glucose tolerance and increased adiponectin levels. Whilst these mice show the same increased longevity as their progenitors they do not show any further increases in longevity [4374].
Humans with mutations in GHR suffer from Laron syndrome, which is characterized by short stature and a similar phenotype to GHR knockout mice. Whether the ageing process is modified in patients with Laron syndrome remains unclear [1345]. One study found evidence of cancer protection in individuals with GHR deficiency, but a normal lifespan [2035]. The d3-GHR genetic polymorphism modulates GH1 sensitivity in humans and has been found to positively affect male longevity. Multivariate regression analysis indicates that being d3 homozygous could add up to 10 years to male lifespan. Homozygous individuals also showed lower serum IGF1 levels [4508].
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 5p13-p12
- Location
- 42,423,775 bp to 42,721,878 bp
- Orientation
- Plus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000187; activation of MAPK activity
GO:0000255; allantoin metabolic process
GO:0006101; citrate metabolic process
GO:0006103; 2-oxoglutarate metabolic process
GO:0006105; succinate metabolic process
GO:0006107; oxaloacetate metabolic process
GO:0006549; isoleucine metabolic process
GO:0006573; valine metabolic process
GO:0006600; creatine metabolic process
GO:0006631; fatty acid metabolic process
GO:0006897; endocytosis
GO:0007259; JAK-STAT cascade
GO:0019221; cytokine-mediated signaling pathway
GO:0019530; taurine metabolic process
GO:0032870; cellular response to hormone stimulus
GO:0040014; regulation of multicellular organism growth
GO:0040018; positive regulation of multicellular organism growth
GO:0042517; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat3 protein
GO:0042523; positive regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat5 protein
GO:0042977; activation of JAK2 kinase activity
GO:0044236; multicellular organism metabolic process
GO:0046449; creatinine metabolic process
GO:0048009; insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway
GO:0050731; positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation
GO:0060396; growth hormone receptor signaling pathway
GO:0060397; JAK-STAT cascade involved in growth hormone signaling pathway
Cellular component: GO:0005576; extracellular region
GO:0005615; extracellular space
GO:0005622; intracellular
GO:0005886; plasma membrane
GO:0005887; integral component of plasma membrane
GO:0009986; cell surface
GO:0016021; integral component of membrane
GO:0043235; receptor complex
GO:0070195; growth hormone receptor complex
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0004896; cytokine receptor activity
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0017046; peptide hormone binding
GO:0019901; protein kinase binding
GO:0042803; protein homodimerization activity
GO:0070064; proline-rich region binding
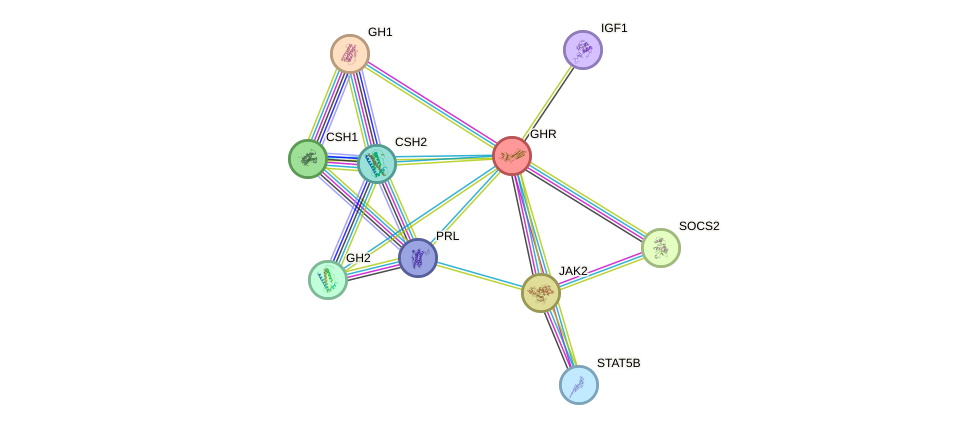
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- GHR, SHC1, PTPN11, STAT5B, STAT3, STAT5A, GH1, PTPN1, GRB2, JAK2, STUB1, SOCS2
- STRING interaction network
Retrieve sequences for GHR
Homologs in model organisms
In other databases
- GenAge model organism genes
- A homolog of this gene for Mus musculus is present as Ghr
- GenDR gene expression
- A homolog of this gene for Mus musculus is present as Ghr
- GenDR gene manipulations
- A homolog of this gene for Mus musculus is present as Ghr
- LongevityMap
- This gene is present as GHR