GenAge entry for BAX (Homo sapiens)
Gene name (HAGRID: 119)
- HGNC symbol
- BAX
- Aliases
- BCL2L4
- Common name
- BCL2-associated X protein
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on evidence showing that the gene product to be a target of genes previously linked to ageing
- Description
An important player in apoptosis, BAX encodes multiple transcripts and has been linked to development, cancer, and age-related changes in apoptosis [600]. Inactivation of BAX in mice extended fertile potential and minimized age-related health problems, including bone and muscle loss, excess fat deposition, alopecia, cataracts, deafness, increased anxiety, and selective attention deficit. It did not extend lifespan [1927]. Changes in apoptotic proteins like BAX could also contribute to ageing-associated atrophy in the skeletal muscle of rats [1639]. It is not known how these processes are related to human ageing, but a role of BAX in human ageing is a possibility.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 19q13.3-q1
- Location
- 48,954,860 bp to 48,961,262 bp
- Orientation
- Plus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0001541; ovarian follicle development
GO:0001764; neuron migration
GO:0001777; T cell homeostatic proliferation
GO:0001782; B cell homeostasis
GO:0001783; B cell apoptotic process
GO:0001822; kidney development
GO:0001836; release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
GO:0001844; protein insertion into mitochondrial membrane involved in apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:0001974; blood vessel remodeling
GO:0002262; myeloid cell homeostasis
GO:0002352; B cell negative selection
GO:0002358; B cell homeostatic proliferation
GO:0002904; positive regulation of B cell apoptotic process
GO:0006687; glycosphingolipid metabolic process
GO:0006808; regulation of nitrogen utilization
GO:0006915; apoptotic process
GO:0006919; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process
GO:0006977; DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator resulting in cell cycle arrest
GO:0006987; activation of signaling protein activity involved in unfolded protein response
GO:0007281; germ cell development
GO:0008053; mitochondrial fusion
GO:0008625; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors
GO:0008630; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage
GO:0008635; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process by cytochrome c
GO:0008637; apoptotic mitochondrial changes
GO:0009566; fertilization
GO:0009636; response to toxic substance
GO:0009651; response to salt stress
GO:0010248; establishment or maintenance of transmembrane electrochemical gradient
GO:0010332; response to gamma radiation
GO:0016032; viral process
GO:0021854; hypothalamus development
GO:0021987; cerebral cortex development
GO:0032091; negative regulation of protein binding
GO:0032461; positive regulation of protein oligomerization
GO:0032469; endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis
GO:0032471; negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion concentration
GO:0032976; release of matrix enzymes from mitochondria
GO:0033137; negative regulation of peptidyl-serine phosphorylation
GO:0033599; regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation
GO:0034644; cellular response to UV
GO:0035234; ectopic germ cell programmed cell death
GO:0042475; odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth
GO:0042981; regulation of apoptotic process
GO:0043065; positive regulation of apoptotic process
GO:0043496; regulation of protein homodimerization activity
GO:0043497; regulation of protein heterodimerization activity
GO:0043524; negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process
GO:0043525; positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process
GO:0043653; mitochondrial fragmentation involved in apoptotic process
GO:0045136; development of secondary sexual characteristics
GO:0046666; retinal cell programmed cell death
GO:0048087; positive regulation of developmental pigmentation
GO:0048147; negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation
GO:0048515; spermatid differentiation
GO:0048597; post-embryonic camera-type eye morphogenesis
GO:0048678; response to axon injury
GO:0048873; homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue
GO:0051259; protein oligomerization
GO:0051260; protein homooligomerization
GO:0051281; positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol
GO:0051402; neuron apoptotic process
GO:0051881; regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential
GO:0060011; Sertoli cell proliferation
GO:0060041; retina development in camera-type eye
GO:0060058; positive regulation of apoptotic process involved in mammary gland involution
GO:0060068; vagina development
GO:0070059; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress
GO:0070242; thymocyte apoptotic process
GO:0070584; mitochondrion morphogenesis
GO:0072332; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator
GO:0090200; positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria
GO:0097190; apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:0097191; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:0097192; extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand
GO:0097193; intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:0097296; activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:1900103; positive regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response
GO:1901030; positive regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:1902262; apoptotic process involved in blood vessel morphogenesis
GO:1902263; apoptotic process involved in embryonic digit morphogenesis
GO:1902445; regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in programmed necrotic cell death
GO:1902512; positive regulation of apoptotic DNA fragmentation
GO:1903896; positive regulation of IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response
GO:1990117; B cell receptor apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:2001234; negative regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway
GO:2001241; positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand
GO:2001244; positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway
Cellular component: GO:0005634; nucleus
GO:0005635; nuclear envelope
GO:0005737; cytoplasm
GO:0005739; mitochondrion
GO:0005741; mitochondrial outer membrane
GO:0005757; mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex
GO:0005783; endoplasmic reticulum
GO:0005789; endoplasmic reticulum membrane
GO:0005829; cytosol
GO:0016020; membrane
GO:0046930; pore complex
GO:0070062; extracellular exosome
GO:0097136; Bcl-2 family protein complex
GO:0097144; BAX complex
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0008289; lipid binding
GO:0015267; channel activity
GO:0030544; Hsp70 protein binding
GO:0042802; identical protein binding
GO:0042803; protein homodimerization activity
GO:0046982; protein heterodimerization activity
GO:0051087; chaperone binding
GO:0051434; BH3 domain binding
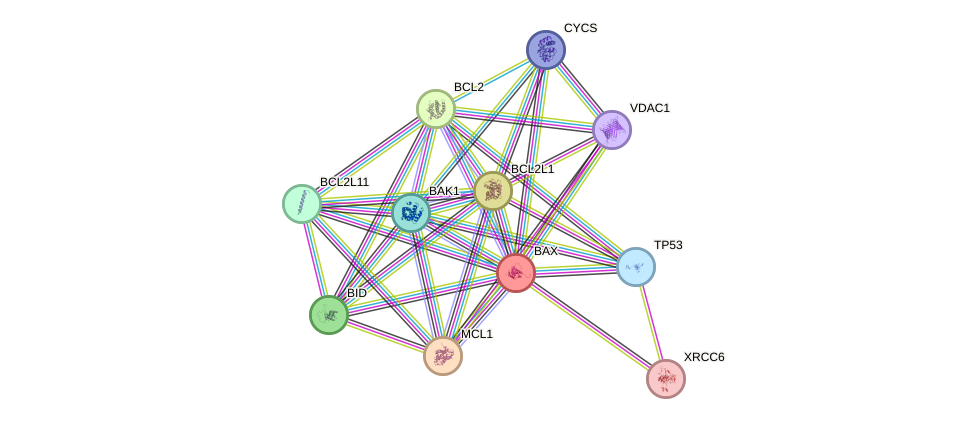
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- TP53, BCL2, VCP, ERCC6, XRCC5, XRCC6, BAX, PRDX1, HSPD1, CLU, KCNA3, BAK1
- STRING interaction network
Retrieve sequences for BAX
Homologs in model organisms
In other databases
- GenAge model organism genes
- A homolog of this gene for Mus musculus is present as Bax
- LongevityMap
- This gene is present as BAX