GenAge entry for MED1 (Homo sapiens)
Gene name (HAGRID: 173)
- HGNC symbol
- MED1
- Aliases
- PBP; TRAP220; RB18A; DRIP230; CRSP200; CRSP1; TRIP2; PPARGBP; PPARBP
- Common name
- mediator complex subunit 1
Potential relevance to the human ageing process
- Main reason for selection
- Entry selected based on indirect or inconclusive evidence linking the gene product to ageing in humans or in one or more model systems
- Description
MED1 is a transcriptional coactivator involved in embryonic development and important for SP1 activity [785]. MED1-null mice die at embryonic stages [785]. Certain age-related pathologies, such as heart disease, may be related to PPARs [392], but it unclear whether MED1 is a major player in human ageing.
Cytogenetic information
- Cytogenetic band
- 17q12
- Location
- 39,404,285 bp to 39,451,274 bp
- Orientation
- Minus strand
Protein information
- Gene Ontology
-
Process: GO:0000122; negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
GO:0000902; cell morphogenesis
GO:0001525; angiogenesis
GO:0001889; liver development
GO:0001892; embryonic placenta development
GO:0002088; lens development in camera-type eye
GO:0002154; thyroid hormone mediated signaling pathway
GO:0003222; ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis
GO:0003406; retinal pigment epithelium development
GO:0006356; regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase I promoter
GO:0006367; transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter
GO:0006590; thyroid hormone generation
GO:0006702; androgen biosynthetic process
GO:0007420; brain development
GO:0007595; lactation
GO:0010628; positive regulation of gene expression
GO:0010839; negative regulation of keratinocyte proliferation
GO:0016567; protein ubiquitination
GO:0030216; keratinocyte differentiation
GO:0030224; monocyte differentiation
GO:0030518; intracellular steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway
GO:0030521; androgen receptor signaling pathway
GO:0031100; animal organ regeneration
GO:0033148; positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway
GO:0033160; positive regulation of protein import into nucleus, translocation
GO:0033601; positive regulation of mammary gland epithelial cell proliferation
GO:0035050; embryonic heart tube development
GO:0035116; embryonic hindlimb morphogenesis
GO:0035162; embryonic hemopoiesis
GO:0035357; peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway
GO:0035729; cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus
GO:0035855; megakaryocyte development
GO:0042789; mRNA transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
GO:0043066; negative regulation of apoptotic process
GO:0044255; cellular lipid metabolic process
GO:0045444; fat cell differentiation
GO:0045618; positive regulation of keratinocyte differentiation
GO:0045648; positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation
GO:0045665; negative regulation of neuron differentiation
GO:0045893; positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
GO:0045944; positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter
GO:0048821; erythrocyte development
GO:0048822; enucleate erythrocyte development
GO:0051726; regulation of cell cycle
GO:0060335; positive regulation of interferon-gamma-mediated signaling pathway
GO:0060744; mammary gland branching involved in thelarche
GO:0060745; mammary gland branching involved in pregnancy
GO:0060750; epithelial cell proliferation involved in mammary gland duct elongation
GO:0070318; positive regulation of G0 to G1 transition
GO:0070371; ERK1 and ERK2 cascade
GO:0070562; regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway
GO:0071364; cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus
GO:0071383; cellular response to steroid hormone stimulus
GO:0097067; cellular response to thyroid hormone stimulus
GO:2000273; positive regulation of receptor activity
GO:2000347; positive regulation of hepatocyte proliferation
GO:2001141; regulation of RNA biosynthetic process
Cellular component: GO:0000151; ubiquitin ligase complex
GO:0000785; chromatin
GO:0005634; nucleus
GO:0005654; nucleoplasm
GO:0005730; nucleolus
GO:0016020; membrane
GO:0016592; mediator complex
GO:0032993; protein-DNA complex
Hide GO termsFunction: GO:0000978; RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding
GO:0000981; RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding
GO:0001047; core promoter binding
GO:0001104; RNA polymerase II transcription cofactor activity
GO:0003682; chromatin binding
GO:0003712; transcription cofactor activity
GO:0003713; transcription coactivator activity
GO:0004872; receptor activity
GO:0005515; protein binding
GO:0008134; transcription factor binding
GO:0016922; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor binding
GO:0030331; estrogen receptor binding
GO:0030374; ligand-dependent nuclear receptor transcription coactivator activity
GO:0030375; thyroid hormone receptor coactivator activity
GO:0031490; chromatin DNA binding
GO:0035257; nuclear hormone receptor binding
GO:0036033; mediator complex binding
GO:0042809; vitamin D receptor binding
GO:0042974; retinoic acid receptor binding
GO:0042975; peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding
GO:0046966; thyroid hormone receptor binding
GO:0050693; LBD domain binding
GO:0061630; ubiquitin protein ligase activity
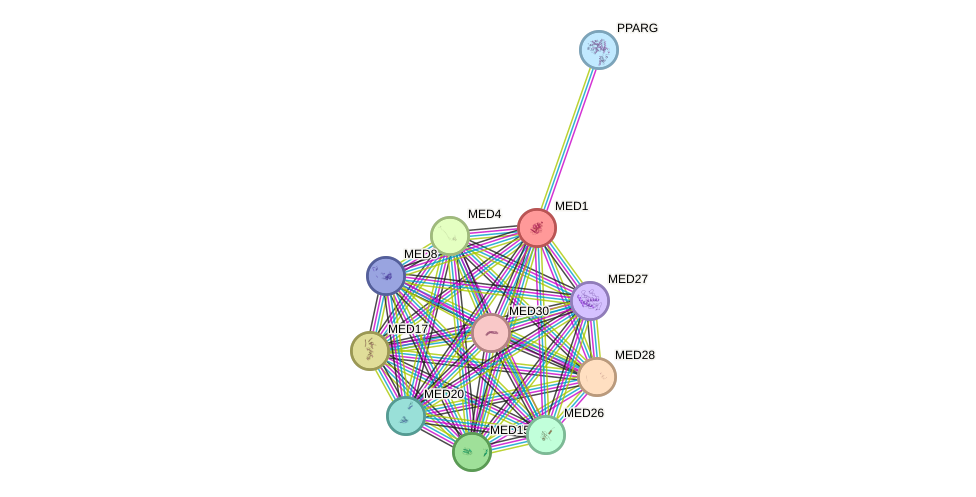
Protein interactions and network
- Protein-protein interacting partners in GenAge
- POU1F1, TP53, ATM, MYC, PARP1, PIN1, NR3C1, AR, MED1, MDM2, ESR1, PPARGC1A, PPARG
- STRING interaction network